NIST 800-30 / OWASP Risk Rating
Security Risk Analysis
Equivalent to the horizontal activity:
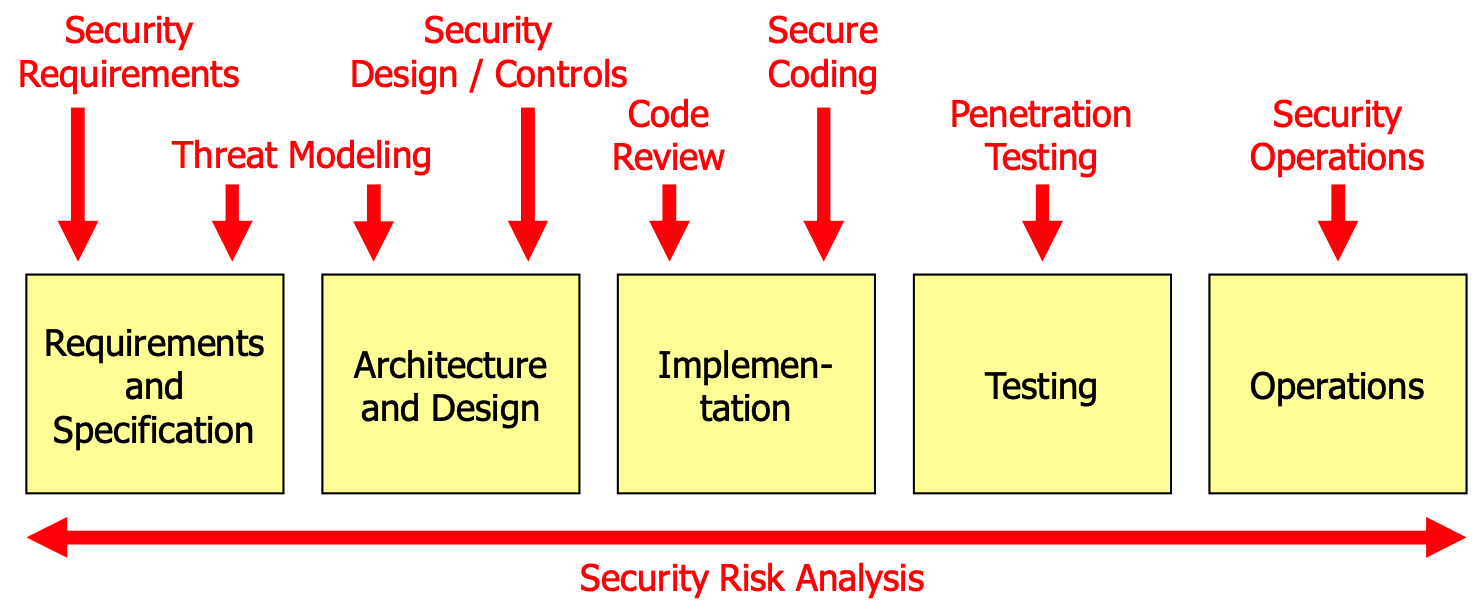
It is used...
- During threat modeling, to rate the risk of the identified threats
- During code reviews, to rate the risk of a discovered security bug
- During penetration testing, to rate the risk of a discovered vulnerability
- During operations, to rate the risk of operational issues
- E.g., to decide whether redundant systems should be used and how frequently backups should be made
Quantitative Risk Analysis
Express risk as financial loss, e.g., in terms of the cost of a data breach.
\[\mathrm{ALE}=\mathrm{SLE}\cdot\mathrm{ARO}\]
- \(\mathrm{ALE}\): Annualized Loss Expectancy
- \(\mathrm{SLE}\): Single Loss Expectancy
- \(\mathrm{ARO}\): Annualized Rate of Occurrence
E.g. we assume that the database is compromised every 5 years and it costs CHF 100'000: ALE = 1/5 * 100'000 = CHF 20'000
However, it's very difficult to estimate the SLE and ARO.
Qualitative Risk Analysis
Process
- Identify security vulnerabilities that should be risk-rated (e.g. by doing threat modeling, penetration testing, code review, etc.)
- Estimate the likelihood of the vulnerability being exploited and its business impact
- Determine the risk based on likelihood and impact
- Risk mitigation: Decide which actions should be taken
NIST 800-30
To determine the likelihood of a successful attack, the following levels are used:

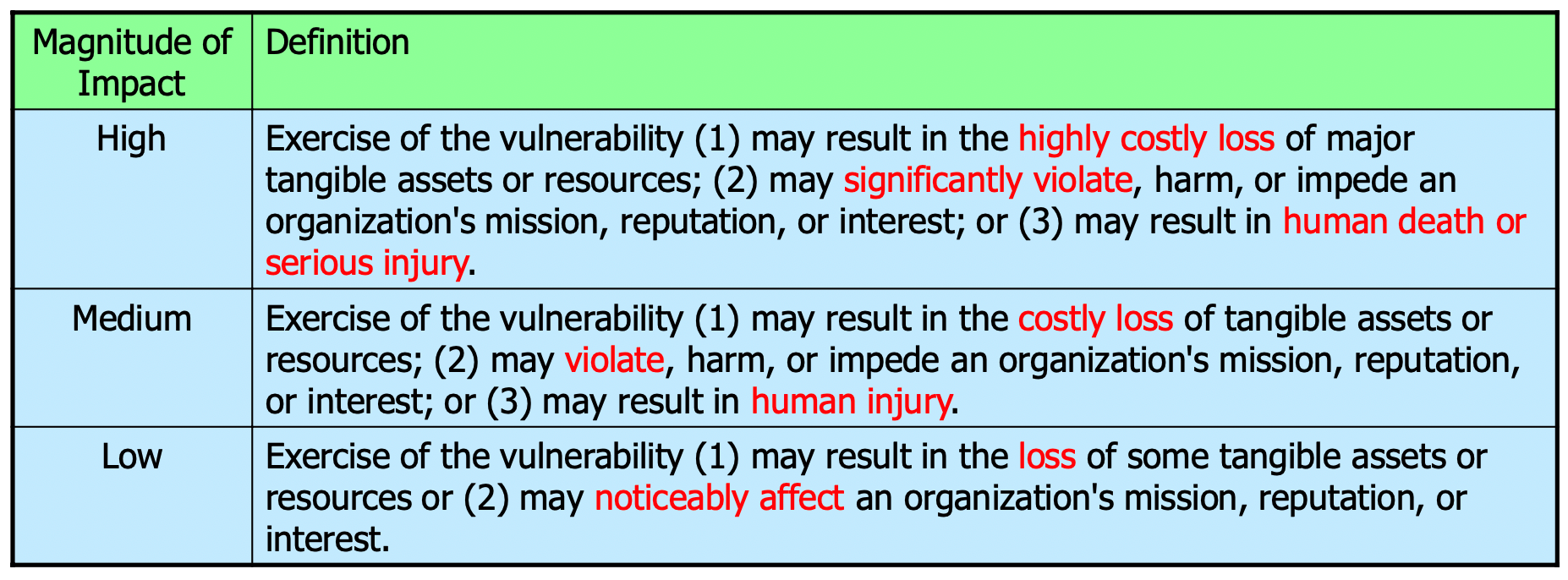
To determine the impact of a successful attack, the following levels are used:
The overall risk is then determined by the following matrix:
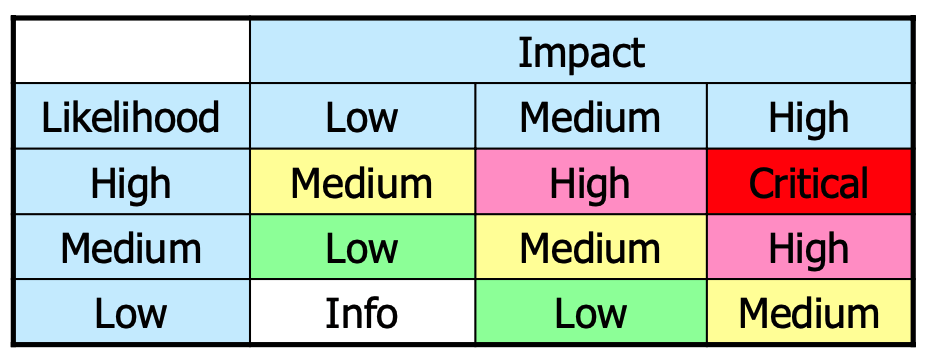
- Critical – absolute need for corrective measures; an existing system should no longer be operated until corrective actions are implemented
- High – strong need for corrective measures; an existing system may continue to operate if really needed, but corrective actions should be implemented as soon as possible (e.g., days to at most a few weeks)
- Medium – indicates that corrective actions are needed and should be implemented within a reasonable time (e.g., next major release)
- Low – indicates that the system's decision authorities must determine whether corrective actions are needed or decide to accept the risk
- Info – the risk can be accepted
OWASP Risk Rating Methodology
Threat Agent Factors
- Skill level: How technically skilled is this group of threat agents?
- No technical skills (1), some technical skills (3), advanced computer user skills (4), network and programming skills (6), security penetration skills (9)
- Motive: How motivated is this group of threat agents to find and exploit this vulnerability?
- Low or no reward (1), possible reward (4), high reward (9)
- Opportunity: What conditions and resources are required for this group of threat agents to find and exploit this
vulnerability?
- Full access or expensive resources required (0), special access or resources required (4), some access or resources required (7), no access or resources required (9)
- Size: How large is this group of threat agents?
- Developers (2), system administrators (2), intranet users (4), partners (5), authenticated users (6), anonymous Internet users (9)
Vulnerability Factors
- Ease of discovery: How easy is it for this group of threat agents to discover this vulnerability (just finding it,
not
yet exploiting it)?
- Practically impossible (1), difficult (3), easy (7), automated tools available (9)
- Ease of exploit: How easy is it for this group of threat agents to actually exploit this vulnerability (once it has
been found)?
- Theoretical (1), difficult (3), easy (7), automated tools available (9)
- Awareness: How well known is this vulnerability to this group of threat agents («how much do the attackers suspect»
that the vulnerability may exist)?
- Unknown (1), hidden (4), obvious (6), public knowledge (9)
- Intrusion detection: How likely is an exploit to be detected?
- Active detection in application (1), logged and reviewed (3), logged without review (8), not logged (9)
(Business) Impact Factors
- Financial damage: How much financial damage will result from an exploit (direct damage by the attack and effort to
recover from it)?
- Less than the cost to fix the vulnerability (1), minor effect on annual profit (3), significant effect on annual profit (7), bankruptcy (9)
- Reputation damage: Would an exploit result in reputation damage that would harm the business (long-term damage)?
- Minimal damage (1), Loss of major accounts (4), loss of goodwill (5), brand damage (9)
- Non-compliance: How much will regulations by governments (e.g., laws) or other companies be violated by an exploit?
- Minor violation (2), clear violation (5), high profile violation (7)
- Privacy violation: How much personally identifiable information could be disclosed?
- One individual (3), hundreds of people (5), thousands of people (7), millions of people (9)
Overall Risk Rating
The overall risk rating is determined by taking the average of the three factors:
\[\mathrm{Threat Agent Likelihood} = \frac{\sum \mathrm{Threat Agent Factors}}{4}\] \[\mathrm{Vulnerability Likelihood} = \frac{\sum \mathrm{Vulnerability Factors}}{4}\] \[\mathrm{Overall Likelihood} = \frac{\mathrm{Threat Agent Likelihood} + \mathrm{Vulnerability Likelihood}}{2}\]
\[\mathrm{Overall Impact} = \frac{\sum \mathrm{Impact Factors}}{3}\]
and then evaluated using the matrix:

The overall risk rating is then determined by the following matrix:
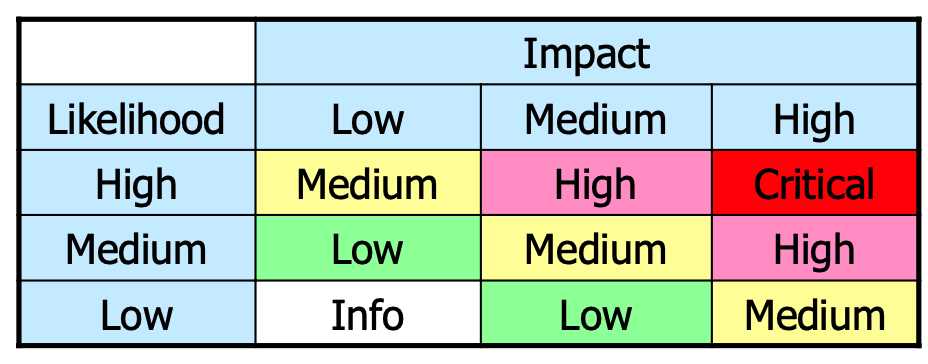
Risk Mitigation
Once the risk has been determined, the following actions can be taken:
- Prioritize the risks
- Decide what to do
- Propose, design, and implement corrective actions
- Update risk analysis documentation
The following options are available:
Risk Acceptance
Accept the risk and do nothing. This is only possible if the risk is low enough.
Risk Reduction
Implement corrective measures to reduce likelihood and/or impact to an acceptable level. This can be done by evaluating the highest factor in the OWASP risk rating and then trying to reduce it.
Risk Avoidance
Avoid the risk by removing the vulnerable component or by removing the vulnerability.
Risk Transfer
Buy insurance or transfer the risk to another party.
Risk Ignorance
Do nothing and hope that the risk will not materialize.