JSF Fundamentals / Secure Database Access / Access Control and Authentication / Custom FORM Authentication / Session Handling and Cookies / JSF View State / Input Validation
Developing Secure Traditional Web Applications
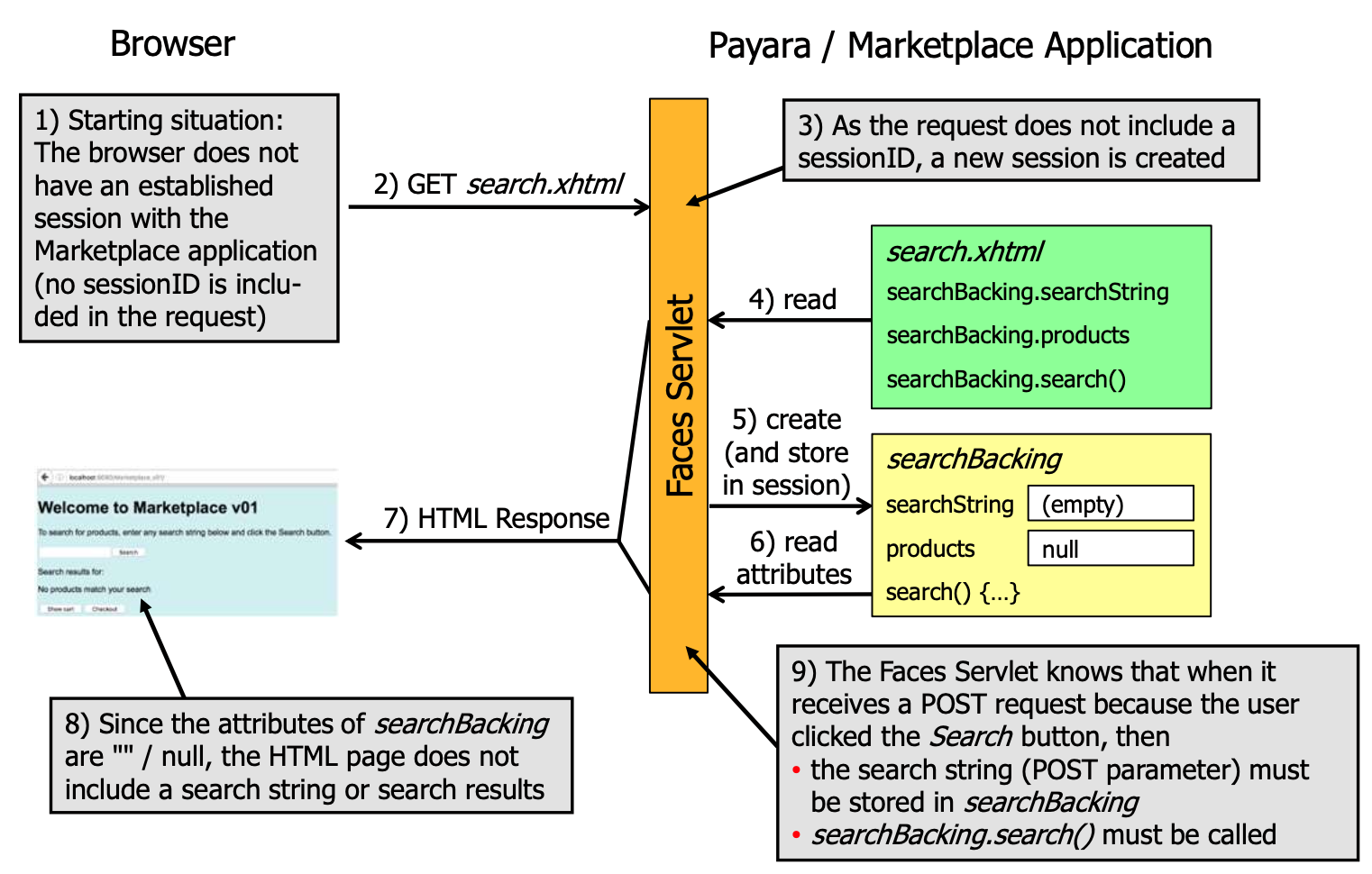
JSF fundamentals
- Facelets: XHTML-based templating language for JSF
- Backing beans: Java classes that contain the logic for the application
- Faces servlet: The servlet that handles all requests to the application
Beans 🫘
Example for a Product page:
public class Product {
private String code;
private String description;
private double price;
public String getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(String code) {
this.code = code;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
// ... the rest of the usual horrible Java boilerplate
@Override
public boolean equals(Object other) { /* ... */ }
}
Database bean
// Marks a CDI bean
@RequestScoped
public class ProductDatabase {
public List<Product> searchProducts(String search) {
// ...
}
}
Backing bean
@Named
@SessionScoped
public class SearchBacking implements Serializable {
private String search;
private List<Product> results;
@Inject
private ProductDatabase database;
public String getSearch() {
return search;
}
public void setSearch(String search) {
this.search = search;
}
public List<Product> getResults() {
return results;
}
public void setResults(List<Product> results) {
this.results = results;
}
public void search() {
results = database.searchProducts(search);
}
}
View
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:h="http://xmlns.jcp.org/jsf/html"
xmlns:f="http://xmlns.jcp.org/jsf/core">
<h:body>
<h:messages globalOnly="true" layout="table"/>
Searched: #{searchBacking.search}
<h:panelGrid columns="2">
<h:outputLabel for="search" value="Search"/>
<h:inputText id="search" value="#{searchBacking.search}"/>
<h:commandButton value="Search" action="#{searchBacking.search}"/>
</h:body>
</html>
Scopes
- Request scope: The bean is created when the request is received and destroyed when the request is finished
- Session scope: The bean is created when the session is created and destroyed when the session is destroyed
- Application scope: The bean is created when the application is started and destroyed when the application is stopped
- Conversation scope: The bean is created when the conversation is started and destroyed when the conversation is ended
- View scope: The bean is created when the view is created and destroyed when the view is destroyed
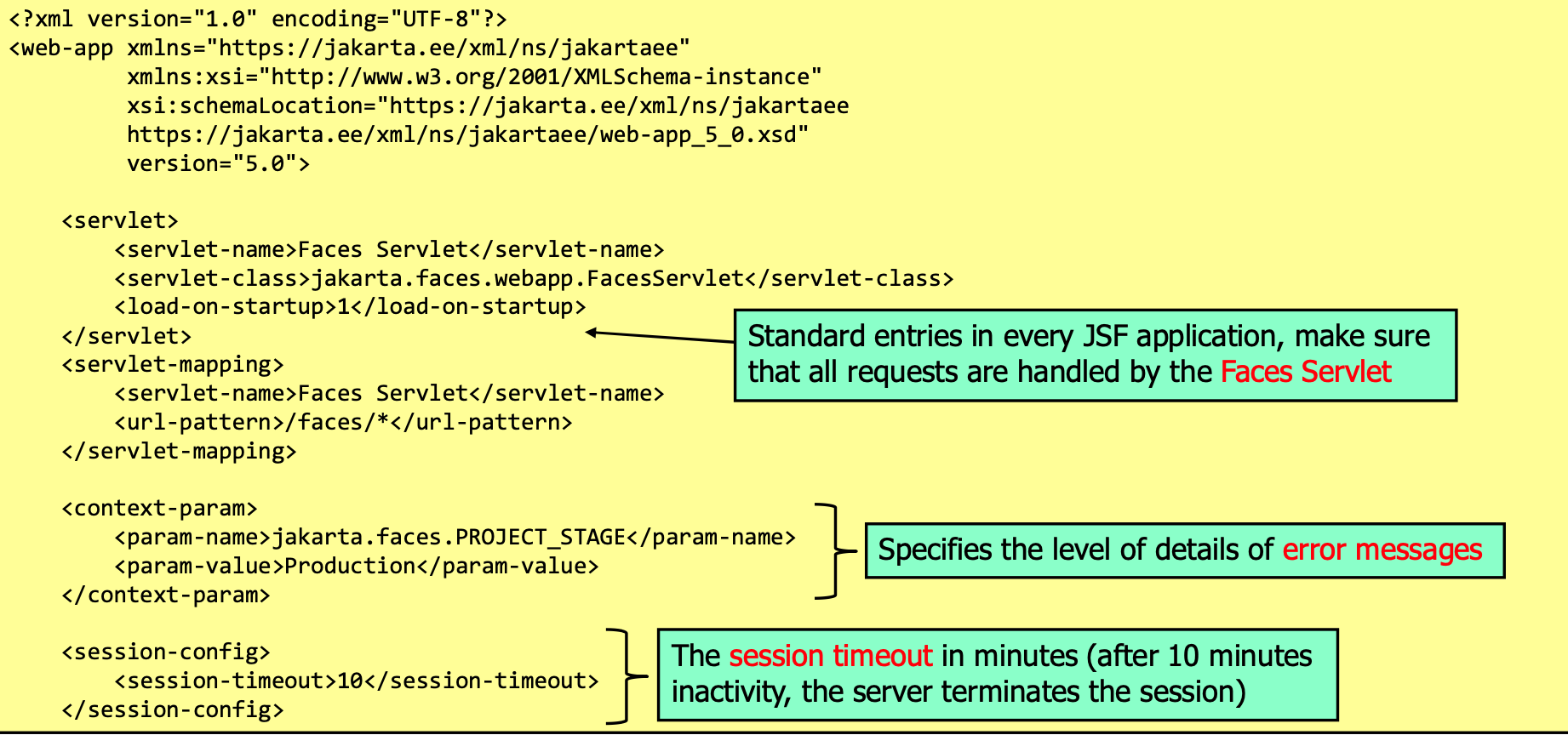
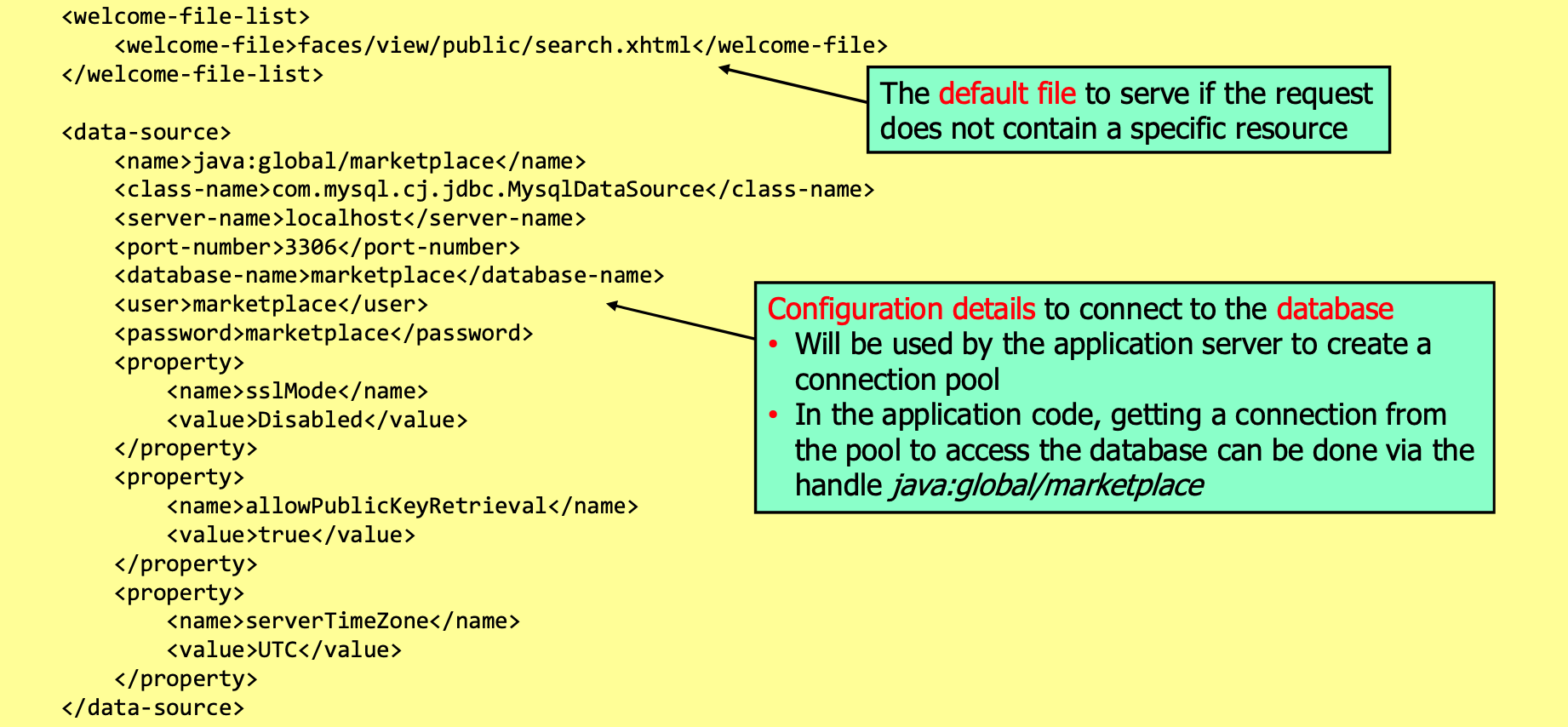
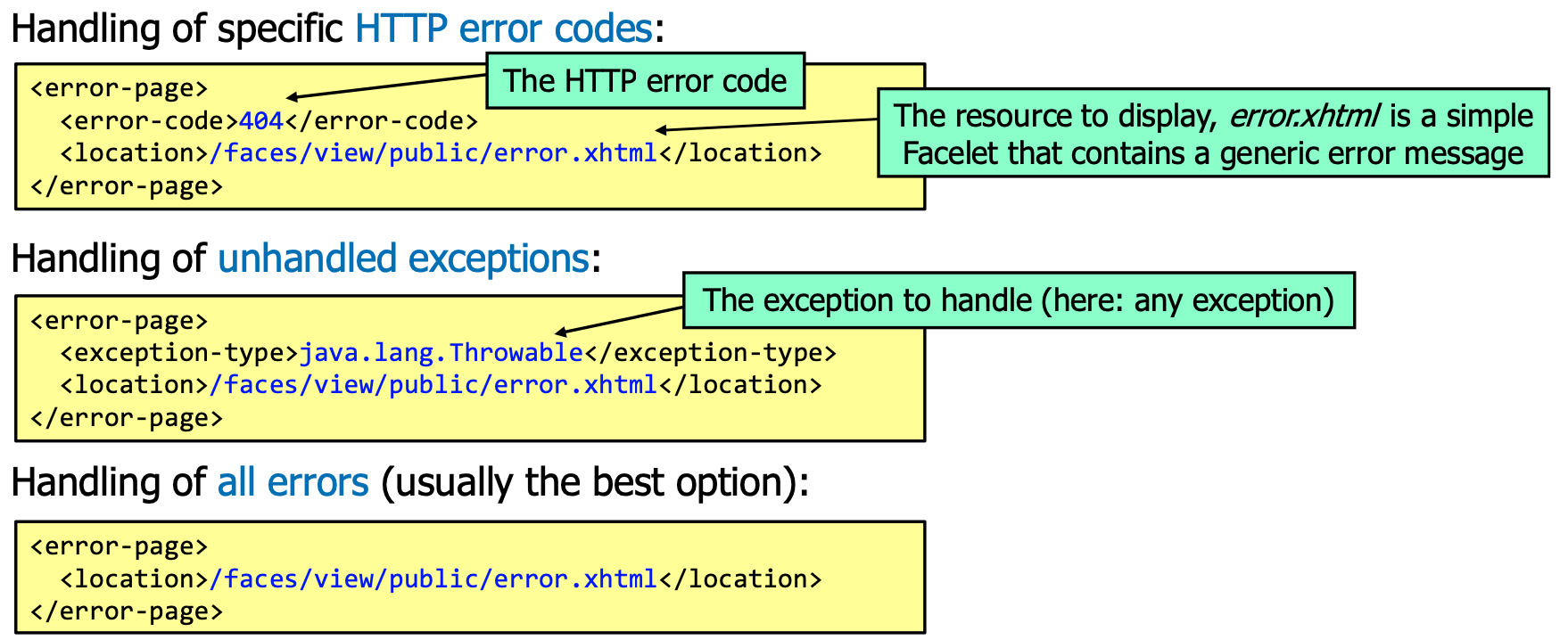
web.xml Configuration

Secure Database Access
Prepared statements
String query = "SELECT * FROM products WHERE code = ?";
try (PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(query)) {
statement.setString(1, code);
try (ResultSet results = statement.executeQuery()) {
while (results.next()) {
// ...
}
}
}
Jakarta Persistence API (Ugly ORM of Java)
@Entity
@Table(name = "products")
@NamedQueries({
@NamedQuery(name = "Product.findAll", query = "SELECT p FROM Product p"),
@NamedQuery(name = "Product.findByCode", query = "SELECT p FROM Product p WHERE p.code = :code")
})
public class Product implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Id private String code;
private String description;
private double price;
// ... the rest of the usual horrible Java boilerplate
@Override
public boolean equals(Object other) { /* ... */ }
}
Configure in persistence.xml:
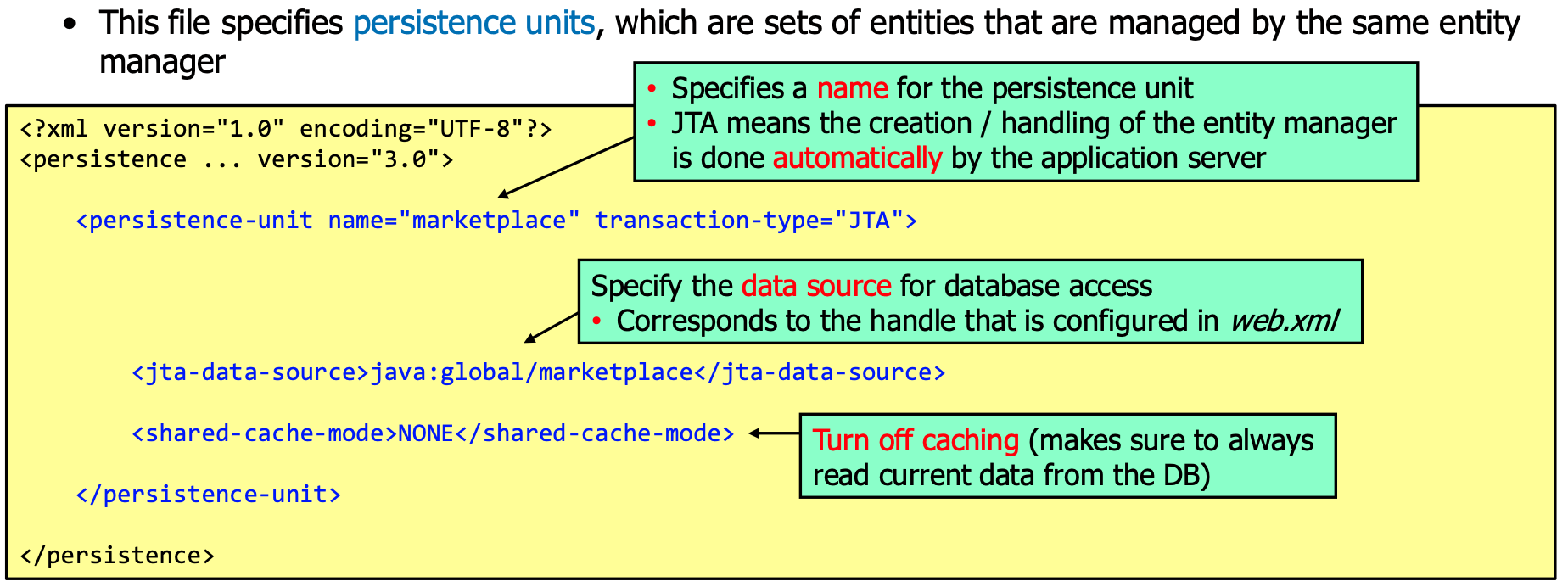
Facade Classes
To provide easy database usage, it's usual to create a facade class that provides methods for the most common database operations:
@Stateless
public class ProductFacade extends AbstractFacade<Product> {
@PersistenceContext(unitName = "marketplace")
private EntityManager em;
public void create(Product product) {
em.persist(product);
}
// ...
public List<Product> findAll() {
return em.createQuery("select object(o) from Product as o").getResultList();
}
public List<Product> findRange(int[] range) {
Query q = em.createQuery("select object(o) from Product as o");
q.setMaxResults(range[1] - range[0]);
q.setFirstResult(range[0]);
return q.getResultList();
}
public List<Product> findByCode(String code) {
Query q = em.createNamedQuery("Product.findByCode");
q.setParameter("code", code);
return q.getResultList();
}
}
Access Control and Authentication
Extending the web.xml
Enable for Basic-Auth:
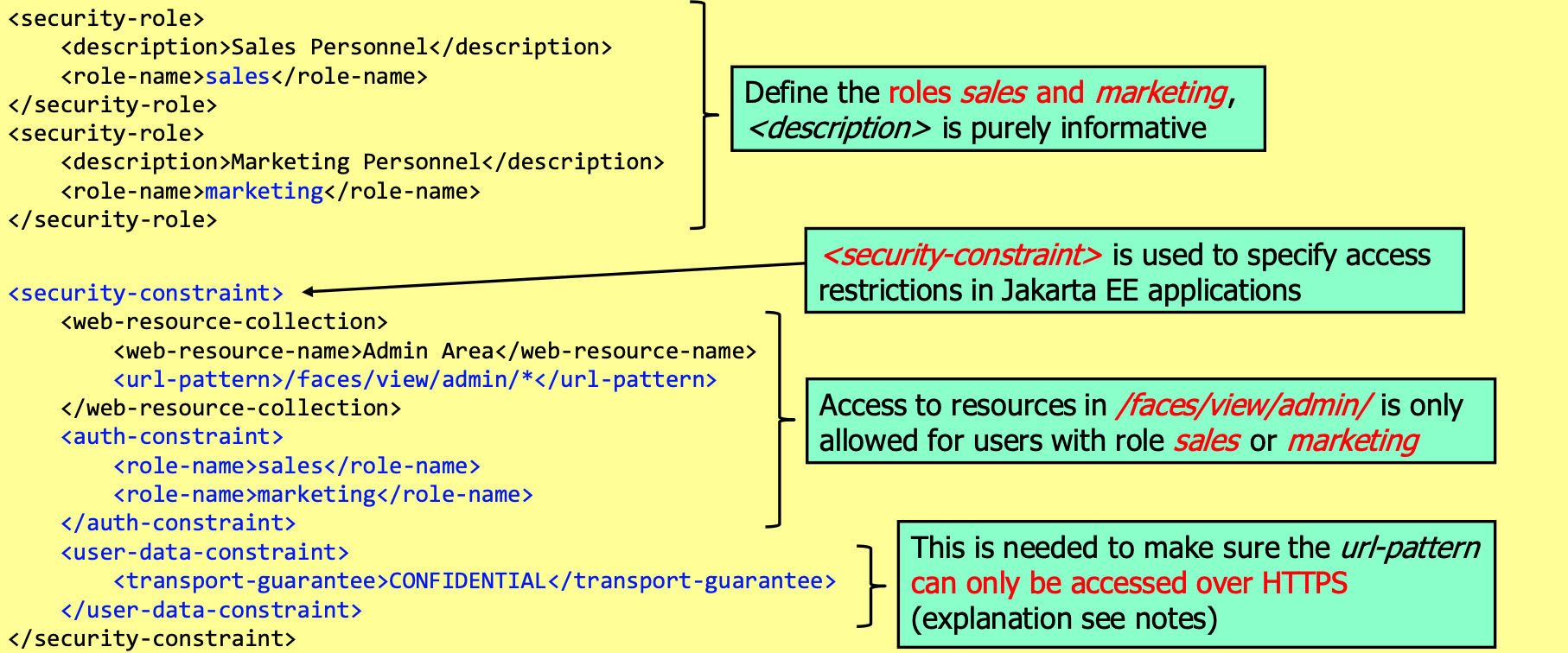
Jakarta EE Security API
@DatabaseIdentityStoreDefinition(
dataSourceLookup = "java:global/marketplace", // Handle to access the database (defined in web.xml)
callerQuery = "SELECT PBKDF2Hash FROM UserInfo WHERE Username = ?", // Query to get the password hash
groupsQuery = "SELECT Rolename FROM UserRole WHERE Username = ?", // Query to get the roles
hashAlgorithm = Pbkdf2PasswordHash.class, // Class of the password hash algorithm
)
@BasicAuthenticationMechanismDefinition(
realmName = "marketplace" // Optionally a name which is displayed to the user
) // Enable basic authentication
@ApplicationScoped // Class can have any name but must be in application scope
public class SecurityConfiguration {
}
Extending to form-based authentication
Add the following to the Security Configuration:
@FormAuthenticationMechanismDefinition(
loginToContinue = @LoginToContinue(
loginPage = "/login.xhtml", // Page to display for login
errorPage = "/login-error.xhtml", // Page to display if login fails
useForwardToLogin = false // Use redirect instead of forward
)
)
Using the corresponding login.xhtml and login-error.xhtml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:h="http://xmlns.jcp.org/jsf/html" xmlns:f="http://xmlns.jcp.org/jsf/core">
<h:head><title>Login</title></h:head>
<h:body>
<form action="j_security_check" method="post">
<h:panelGrid columns="2">
<h:outputLabel for="username" value="Username"/>
<input type="text" id="username" name="j_username"/>
<h:outputLabel for="password" value="Password"/>
<input type="password" id="password" name="j_password"/>
<input type="submit" value="Login"/>
</h:panelGrid>
</form>
</h:body>
</html>
To implement the logout, add the following backing bean:
@Named
@SessionScoped
public class LoginController implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public String logout() {
FacesContext.getCurrentInstance().getExternalContext().getRequest().logout();
return "/index.xhtml?faces-redirect=true";
}
}
Additionally, the following methods can be used to check security features (on request):
String getRemoteUser(); // Returns the username of the currently logged in user
boolean isUserInRole(String role); // Returns true if the user has the given role
Principal getUserPrincipal(); // Returns the principal of the currently logged in user
e.g.
<h:column rendered="#{request.isUserInRole('sales')}">
<h:commandLink value="Sales" action="sales.xhtml"/>
</h:column>
Custom FORM Authentication
@DatabaseIdentityStoreDefinition( /* ... */ )
@CustomFormAuthenticationMechanismDefinition(
loginToContinue = @LoginToContinue(
loginPage = "/login.xhtml",
errorPage = "", // Empty means login page is used
useForwardToLogin = false
),
authenticationParameters = {
@AuthenticationParameter(
name = "username", // Name of the username parameter
required = true
),
@AuthenticationParameter(
name = "password", // Name of the password parameter
required = true
)
}
)
Login facelet
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:h="http://xmlns.jcp.org/jsf/html" xmlns:f="http://xmlns.jcp.org/jsf/core">
<h:head><title>Login</title></h:head>
<h:body>
<h:form>
<h:panelGrid columns="2">
<h:outputLabel for="username" value="Username"/>
<h:inputText id="username" value="#{authenticationBacking.username}"/>
<h:outputLabel for="password" value="Password"/>
<h:inputSecret id="password" value="#{authenticationBacking.password}"/>
<h:commandButton value="Login" action="#{authenticationBacking.login}"/>
</h:panelGrid>
</h:form>
</h:body>
</html>
Backing Bean
public class AuthenticationBacking {
@Inject private SecurityContext securityContext;
private String username;
private String password;
public String login() {
FacesContext context = FacesContext.getCurrentInstance();
Credential credential = new UsernamePasswordCredential(username, new Password(password));
AuthenticationStatus status = securityContext.authenticate(
context.getExternalContext().getRequest(),
context.getExternalContext().getResponse(),
withParams().credential(credential)
);
if (status.equals(AuthenticationStatus.SEND_CONTINUE)) {
context.responseComplete();
} else if (status.equals(AuthenticationStatus.SEND_FAILURE)) {
Message.setMessage("Login failed", FacesMessage.SEVERITY_ERROR);
}
}
// ...
}
Session Handling and Cookies
Example header:
Set-Cookie: session=id=18A8F9C37BEE017A; expires=Wed, 09-Jun-2021 10:18:39 GMT; path=/; HttpOnly; Secure; Domain=example.com
Configure in web.xml:
<session-config>
<session-timeout>30</session-timeout>
<cookie-config>
<http-only>true</http-only> <!-- Default: true in Payara -->
<secure>true</secure>
</cookie-config>
<tracking-mode>COOKIE</tracking-mode> <!-- COOKIE prevents that the session ID is appended to the URL -->
</session-config>
JSF View State
JSF stores a view state in the session, mainly so that the application knows what to do no subsequent requests by linking the received POST request to the actions that have to be performed on the backing bean.
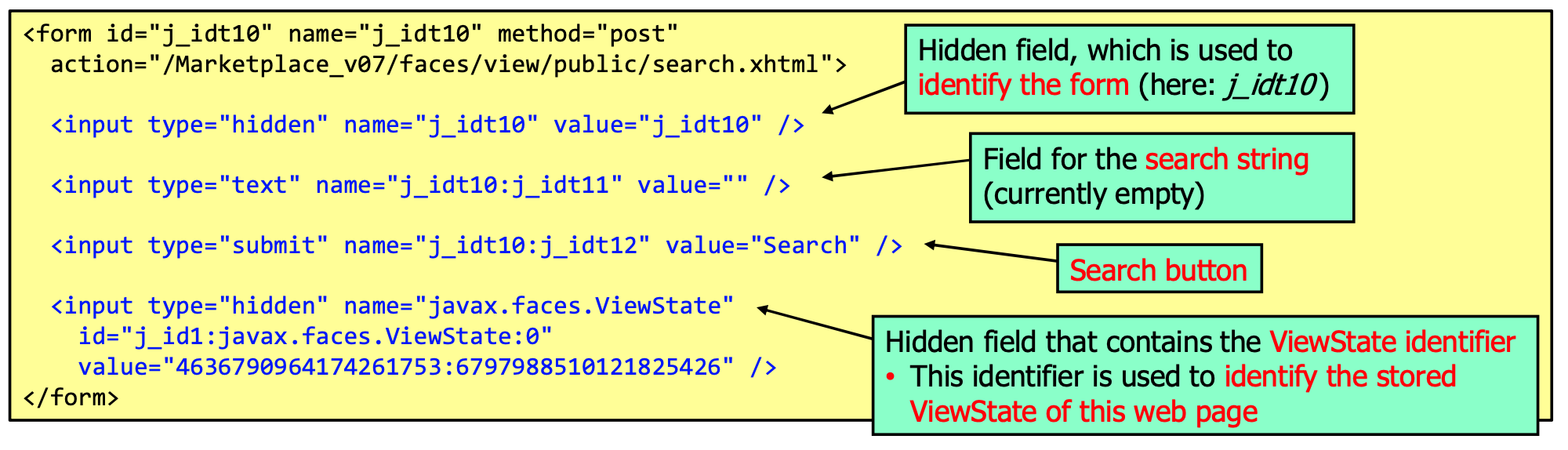
This has the following security relevant implications:
- It prevents forced browsing with POST requests
- It prevents CSRF attacks (with POST requests)
JSF also supports explicit CSRF protection, but this is not enabled by default. To use it, use the following
in faces-config.xml:
<protect-view>
<protect-when>always</protect-when> <!-- Always protect the view, optional -->
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</protect-view>
Input Validation
Example:
public class SearchBacking {
@NotNull
@Size(min = 3, max = 50, message = "Search term must be between 3 and 50 characters")
// @Pattern, @Email, @URL, @Digits, @Past, @Future, @DecimalMax, @DecimalMin, @Max, @Min, @AssertTrue, @AssertFalse
private String search;
@Pattern(regexp = "^[A-Za-z0-9]+$", message = "Only alphanumeric characters allowed")
private String filter;
// ...
}
an in the facelet:
<h:message for="search" errorClass="redBoldUnderlinedItalicText" />
Custom Validators
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Constraint(validatedBy = MyValidator.class)
public @interface CreditCardCheck {
String message() default "Invalid credit card number";
Class<?>[] groups() default {};
Class<? extends Payload>[] payload() default {};
}
public class CreditCardValidator implements ConstraintValidator<CreditCardCheck, String> {
@Override
public void initialize(CreditCardCheck constraintAnnotation) {}
@Override
public boolean isValid(String value, ConstraintValidatorContext context) {
return value != null && value.startsWith("1234") && verySophisticatedValidation(value);
}
}