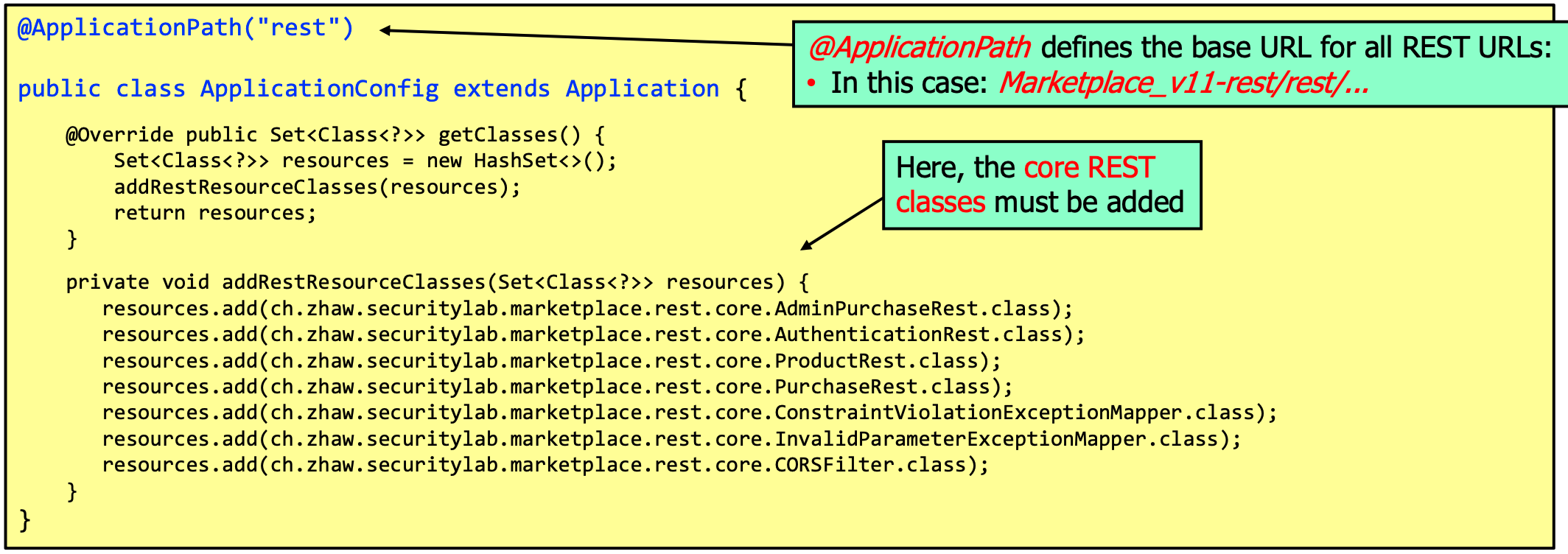
Developing Secure Modern Web Applications
- Basic properties of RESTful web services
- They use HTTP and the 5 methods GET, POST, PUT/PATCH and DELETE to read, create, update and delete resources within the service
- Stateless, there are no sessions, every request must include all information such that the server can process the request
- Resources are identified via meaningful URLs, e.g., /customers to identify all customers and /customers/1234 to identify customer with ID 1234
- To transport data, JSON format is typically used
To set CORS rules:
import jakarta.ws.rs.container.ContainerRequestContext;
import jakarta.ws.rs.container.ContainerResponseContext;
import jakarta.ws.rs.container.ContainerResponseFilter;
import jakarta.ws.rs.ext.Provider;
@Provider
public class CORSFilter implements ContainerResponseFilter {
@Override
public void filter(ContainerRequestContext requestContext, ContainerResponseContext response) {
response.getHeaders().putSingle("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*");
response.getHeaders().putSingle("Access-Control-Allow-Methods", "OPTIONS, GET, POST, PUT, DELETE");
response.getHeaders().putSingle("Access-Control-Allow-Headers", "*");
}
}
DTOs are serializable, use the @JsonbTransient annotation to exclude fields from serialization. Given a `Product
DTO, the service could then be implemented like:
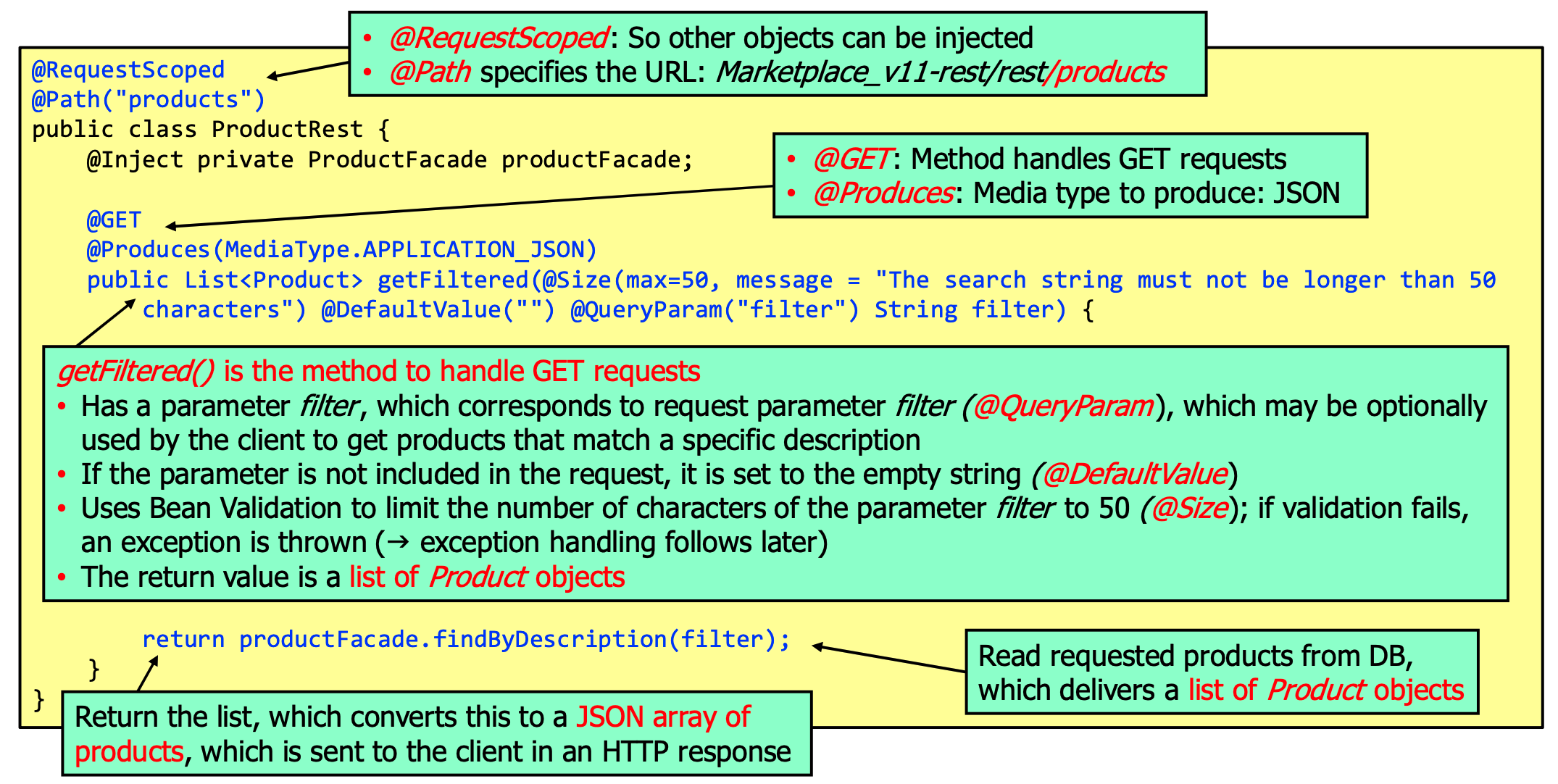
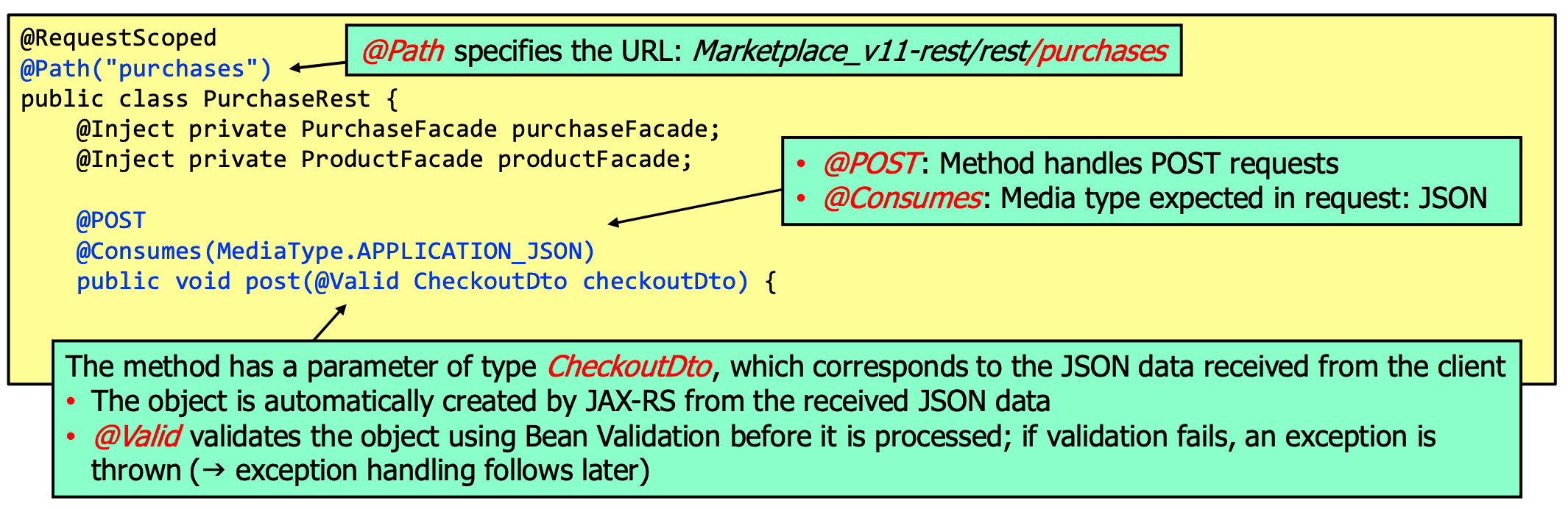
on the admin side:


