Introduction
Motivation
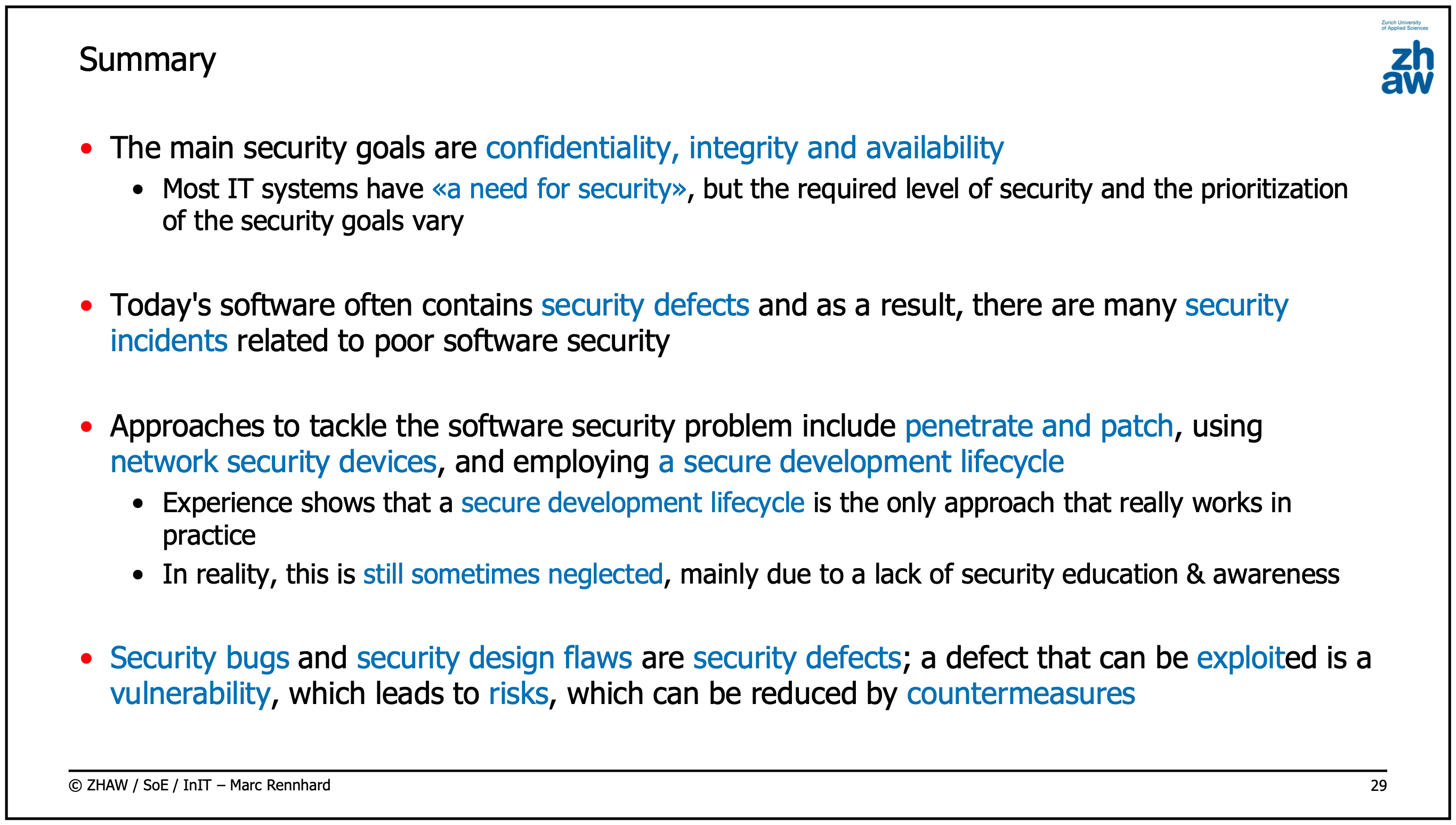
When talking about information security, we consider the following key concepts:
- Confidentiality
- Sensitive data must be protected from unauthorized (read) access
- Integrity
- Sensitive data must be protected from unauthorized (write) access
- Availability
- Sensitive data must be available to authorized users when it is needed
Terms and Definitions
-
Virus
- A program that can copy itself and infect other programs
- The executable programs or documents that are infected are called hosts
-
Worm
- Similar to viruses, but are standalone programs that do not need to infect other programs to spread
- Worms can spread by themselves
-
Trojan
- A program that appears to be harmless, but actually has malicious intent
-
Security Bug
- A security-relevant software problem introduced during implementation of the software
-
Security Design Flaw
- A security-relevant software problem introduced during the design of the software
-
Security Defect
- Both security bugs and security design flaws are called security defects
-
Vulnerability
- A vulnerability is a defect (bug or design flaw) that can be exploited by an attacker
- Not every security-relevant bug or flaw can be exploited, as there may for instance be other safeguards that compensate for the defect
-
Threat
- A threat is a potential danger that might exploit a vulnerability (can be intentional (attacker) or unintentional (accident, e.g. fire in server room))
- The attacker is often identified as threat agent, which the actual attack is the threat action
-
Exploit
- The actual attack that takes advantage of a vulnerability
-
Asset
- Anything (hardware, software, data,...) that is of value to an organization
-
Risk
- Measure of criticality of a specific threat or vulnerability
-
Countermeasure
- An action, device or process that reduces the risk of a specific threat or vulnerability
Problems of Penetrate and Patch:
- If a vulnerability is found, it is often not possible to patch it immediately and the patch itself may introduce new vulnerabilities
- The attacker may have already exploited the vulnerability before the patch is available